Essential trigonometric identities-Physics NEET/JEE/CUET revision
TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES
What exactly is trigonometry?
What are the trigonometric applications?
The trigonometric method is used to determine the height of a building or mountain, as well as the length of a beam required to span a specific distance.
The trigonometry method is used to calculate an object's torque and forces.Engineers use trigonometric methods to solve design and construction problems involving structures such as bridges and buildings.
A navigation method that calculates the distance between a receiver and a satellite using the law of cosines.
Trigonometric methods are used by astronomers to calculate the distances of stars and planets from Earth.
Physicists use trigonometry to study wave behaviour, analyse signals, and predict particle behaviour.used in periodic motion, such as a simple pendulum.
GENERAL TRIANGLE:
A general triangle is a triangle with three sides and three internal angles that is closed in shape. Any triangle's three angles add up to 180 degrees.
RIGHT ANGLE:·
A three-sided figure in a right triangle has one right angle that the sum of the remaining angles is 90 degrees.·
A right triangle has three angles that add up to 180 degrees.
Problem-solving benefits are one of the right triangle's unique qualities.·
It is used in phenomena involving periodic motion,such as basic pendulum oscillations.·
Any problem can be solved using well-known trigonometric laws like the sine and cosine laws.
HYPOTENUSE
The hypotenuse is the side of a right triangle that is opposite the right angle.·
It is the longest of the right triangle's three sides.
The Theory of Pythagoras:
The area of the squares on the hypotenuse is equal to the total area of the squares on the other two sides if we draw a square on the hypotenuse and a square on each of the other sides. is equal to 90 degrees.
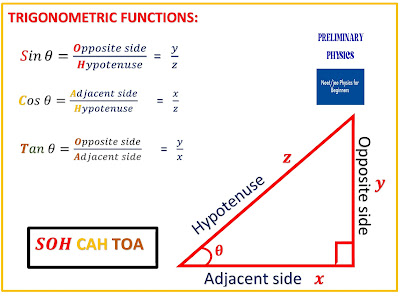
TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS:
THE SINE FUNCTION (Sin symbol)
The sine is the ratio of the opposite side of a right triangle to the hypotenuse.
FUNCTION OF COSINE: (Cos symbol)
The cosine is the ratio of the adjacent side of a right triangle to the hypotenuse.





Comments
Post a Comment